Gross Total Income: A Complete Overview
When you perform a work, all you expect is income to be credited to your bank account on a regular basis. But till, there are a list of taxes that gets deducted from the total income you have earned.
Income tax department of India, has divided income into seven types
- Earned income
- Profit income
- Interest income
- Dividend income
- Rental income
- Capital gains income
- Royalty income

But we still know that, tax is levied on the income that is earned by every individual. Before deducting, the income is referred to as Gross Total Income or GTI. In this article we will look into the significance of GTI.
1. Gross Total Income: Definition
Its simple to understand, Gross Total Income is nothing but the amount earned by a person before taxes are levied. The total amount mentioned in the paycheck earned by an individual.
Gross Total Income is not only the salary earned, but according to Income Tax 1961 an income earned is categorized into five divisions,
- Income earned through salary
- Income earned from rents through property
- Profits and gains from businesses
- Capital gains
- Income from other sources
All these income combined together, before deducting tax is called Gross Total Income. The same for a company or business is referred as gross margin or gross profit because it is the total revenue earned by the organization.
Things included for Gross Total Income:
We just listed out the divisions that can be included for gross total income. But there are few more things that has to taken care of, referring the sections from the Income tax of 1961,
- The income that is earned by an individual should be under the Income Tax clubbing rules adjustments.
- The cash or credit received under section 68 of the Income tax Act, known as Unexplained Tax Credit. This refers to the amount earned by an individual, which doesn’t have any explanation about the sources.
- Investments that are made without valid explanations should also be included for Gross Total Income.
- Assets such as jewellery, money or other items which doesn’t have suitable explanation should also be included. This is in accordance with Section 69A of Income Tax Act.
- Assets that are not disclosed which is known as undisclosed income under Section 69B should also be included.
- According to Section 69C there are certain expenditures that are made which doesn’t have proper explanation.
- According to Section 69D the Hundi amount that is being borrowed or repaid is added to the Gross Total Income.
Overall, it is not only the income that is mentioned in every individual’s paycheck, it is also the amount of money that doesn’t have proper explanation. These categories should also be included for Gross Total Income valuation.
2. Gross Total Income: Calculation
GTI calculation for individuals and businesses vary. Here we will look how it is done for both categories.
a. GTI calculation for an individual:
The entire amount that is mentioned in the paycheck of an employee is taken. This isn’t the only source of income for an individual, he might also have other sources such as investments, stocks etc.
For example,
A person has works in an IT firm. Monthly income from his income is Rs. 75,000. Apart from this he earns Rs. 20,000 from a property as rent. He also owns a dividend share of Rs. 30,000 in a company.
Gross total income = 75,000 + 20,000 + 30,000 = Rs. 1,25,000
b. GTI calculation for a business:
For a business it is not the total income earned by the firm, but instead it is the gross profit made before deduction the taxes. In business, it is the gross margin for a year before expenses, taxes and interests are deducted from the total profit made.
The for calculation GTI is as follows,
Gross Income = Gross Revenue - Cost of goods sold
For example, let’s calculate the Gross income a manufacturing company whose gross revenue is assumed to be Rs. 25,00,000
- Raw materials cost = Rs. 75,000
- Supply costs = Rs. 16,000
- Machinery costs = Rs. 5,00,000
- Labour costs = Rs. 1,50,000
- Packaging costs = Rs. 2,50,000
Gross income = (25,00,000) - (75,000 + 16,000 + 5,00,000 + 1,50,000 + 2,50,000) = 25,00,000 - 9,91,000 = Rs. 15,09,000
3. Difference between Net Income and Gross Income:
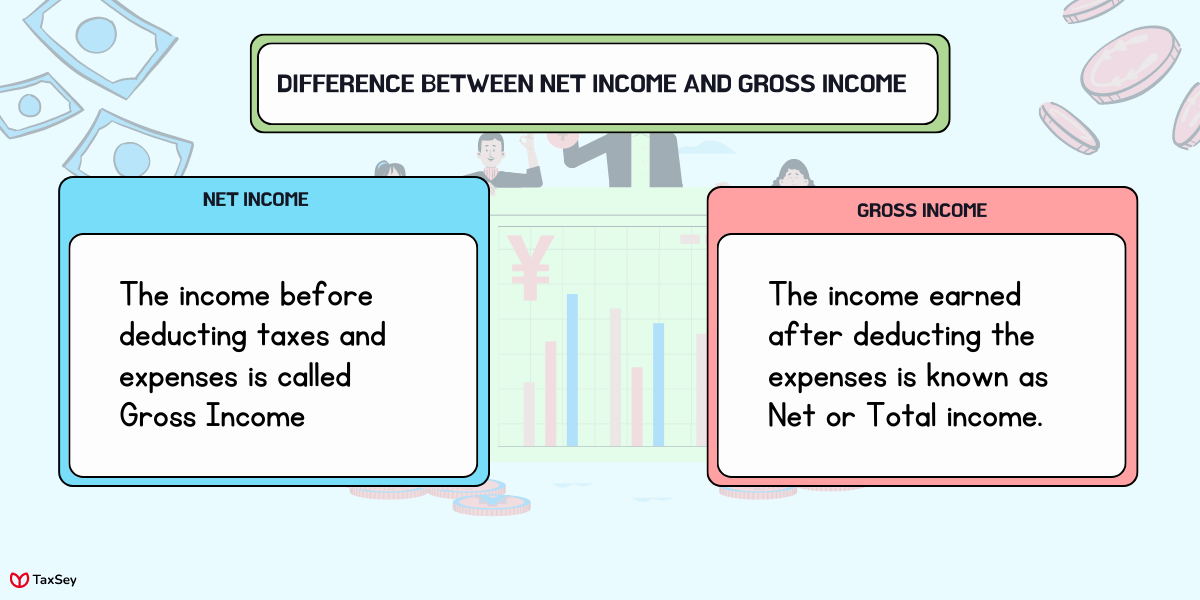
The definition of both Net Income and Gross Income gives us a clear idea of what is the major difference between them.
- The income before deducting taxes and expenses is called Gross Income, whereas the income earned after deducting the expenses is known as Net or Total income.
- Net income is the parameter that determines the profit gain of an individual or a company, as it is the remaining income that is sustained after deduction of taxes.
- If the Net income is positive, then it is said to be profit. If it is negative, then the person is financially weak.
- After calculation Gross Income and Net income, the difference between both can help us analyse the amount of expenses made. If the difference is large, then the company has lot of expenses, which should be reduced.
Conclusion:
An individual will have various sources of income and the income earned may vary for every financial year. Calculating GTI will include all amount earned, including tips, incentives, rent, dividends and much more. By calculating this, it is easy for every person to self analyse the financial gain and loss. This helps in cutting expenditures and making use of the gross income eared in a positive way to gain profit.
Frequently Asked Questions
The goods and services tax (GST) is a value-added tax (VAT) levied on most goods and services sold for domestic consumption.